How plants control their ‘mouths’
Writing for the U.S. National Science Foundation in December 2022, Jared Dashoff described fascinating new research on how plants “breathe.” It’s a “key breakthrough,” he said, with implications for our global food supply in the coming century, as global climate warms. The new research is focused, specifically, on the discovery of an “elusive molecular pathway.” Plants use this in exchanging carbon dioxide and water with the air. Biochemist Julian Schroeder, who led the new work, said his team has found the mechanism by which plants open and close their “mouths.”. Dashoff wrote:
The researchers hope that harnessing this mechanism could lead to future engineering of plant water use efficiency and carbon intake. Critical as atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration continues to increase.
In fact, the researchers have filed a patent. And, they are examining ways to translate their findings into tools for crop breeders and farmers.
The National Science Foundation funded this research from the University of California San Diego and collaborators in Estonia and Finland. They published the new study on December 7, 2022, in the peer-reviewed journal Science Advances.
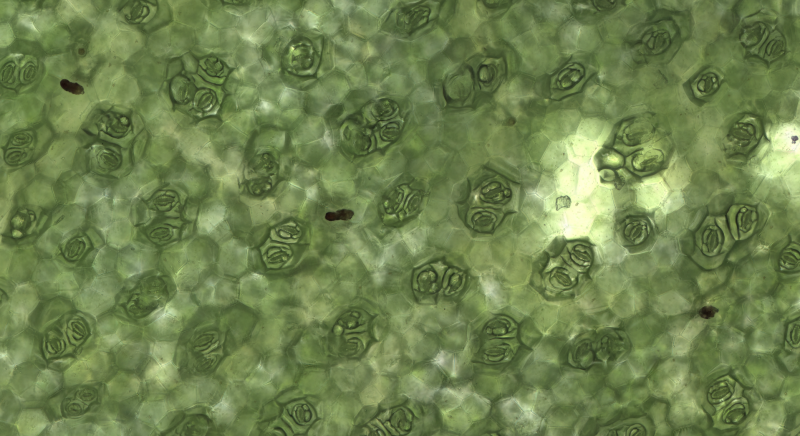
You breathe, I breathe, plants breathe
In Greek, stoma means “mouth.” So basically, plants use the stomata – microscopic cell structures – on their leaves to take in carbon dioxide and water. Then, sunlight turns these into the nutrients plants need to grow. As Dashoff explained:
This process also emits oxygen, which humans and other animals then breathe. That’s the basic summary of photosynthesis. But how exactly does it work?
The process becomes a bit clearer on the microscopic level. Indeed, on the underside of leaves and elsewhere, depending on the plant, are tiny openings called stomata. There are thousands of them per leaf with variations by plant species. Like little castle gates, pairs of cells on the sides of the stomatal pore – known as guard cells – open their central pore to take in the carbon dioxide.
However, when stomata are open, the inside of the plant is exposed to the elements. Consequently, water from the plant is lost into the surrounding air, which can dry out the plant. Plants, therefore, must balance the intake of carbon dioxide with water vapor loss by controlling how long the stomata remain open.
Julian Schroeder commented:
The response to changes is critical for plant growth and regulates how efficient the plant can be in using water. Which is important as we see increased drought and rising temperatures.
What they learned
As a matter of fact, scientists have long understood stomata and the balance between carbon dioxide intake and water loss. But what they haven’t known, until now, is how plants sense carbon dioxide to signal stomata to open and close in response to changing carbon dioxide levels. As Dashoff explained:
If plants, especially crops like wheat, rice and corn, can’t strike a new balance [in a warming world], they risk drying out. Farmers risk losing valuable output. And more people across the world risk going hungry. Even with advances in agriculture, an NSF-funded study in published in 2021 found that global agricultural productivity over the past 60 years is still 21% lower than it could have been without climate change …
Dashoff explained these researchers identified a series of proteins that work, as he said:
… like a chain of soldiers sensing the carbon dioxide level and calling out ‘CLOSE THE GATES!’ to get the guard cells to relax and shut the stomata.
A new understanding of how plants control their ‘mouths’
He said the new understanding of this signaling mechanism will let scientists “edit the signals.” And so, in the future, plants will be able to strike the right balance between taking in carbon dioxide versus losing water. This will allow scientists and plant breeders to produce crops robust enough for the environment of the future.
As this century and the next progress, this knowledge will help scientists devise ways to protect food crops and guard against human hunger.
Bottom line: In new, breakthrough research, scientists have now learned how plants control their “mouths.” That is, they’ve learned the mechanism that lets plants breathe in carbon dioxide.



