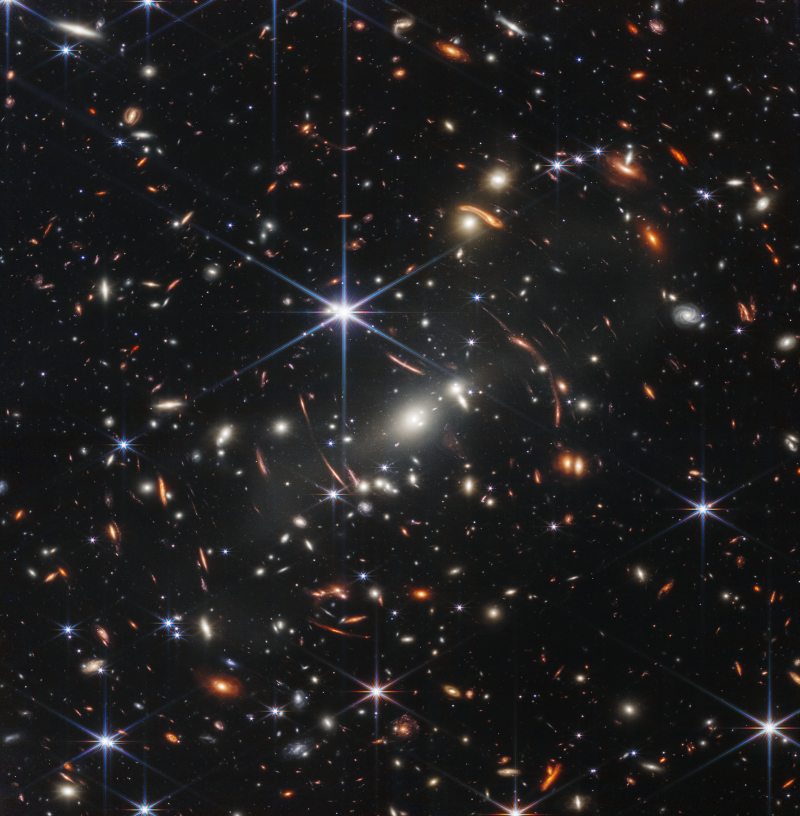
What’s a galaxy?
A galaxy is an unlimited island of fuel, dust and stars in an ocean of space. Usually, galaxies are thousands and thousands of light-years aside. Galaxies are the constructing blocks of our universe. Their distribution isn’t random, as one may suppose. As an alternative, galaxies are alongside unimaginably lengthy filaments throughout the universe, forming a cosmic web of star cities.
A galaxy can comprise a whole bunch of billions of stars and be many 1000’s of light-years throughout. Our personal galaxy, the Milky Way, is round 100,000 light-years in diameter. That’s about 587,900 trillion miles, or practically 1,000,000 trillion kilometers.
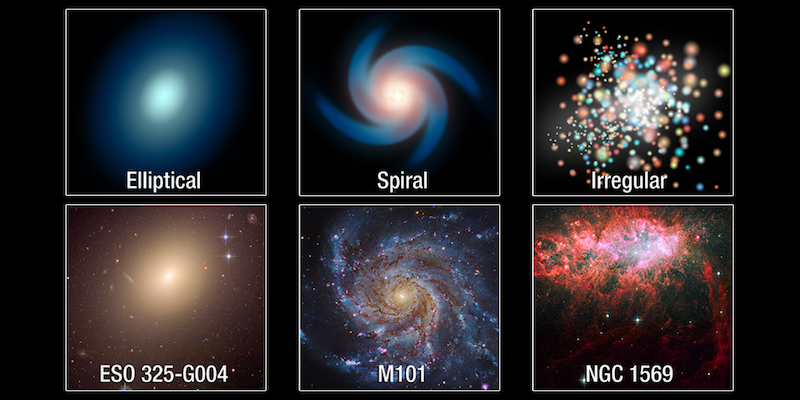
The three kinds of galaxies are spiral, elliptical or irregular.
Galaxy sizes differ extensively, starting from very small to unbelievably monumental. Small dwarf galaxies comprise about 100 million stars and large galaxies comprise greater than a trillion stars.
Additionally, there are an estimated 200 billion galaxies within the universe.
In 2016, utilizing 20 years of photos from the Hubble, it was estimated that there have been in total two trillion or extra galaxies within the observable universe.
In 2021, knowledge from NASA’s New Horizons space probe was used to revise the sooner estimate to roughly 200 billion galaxies. pic.twitter.com/J11gK0Zu4F
— swami (@C8257877) February 24, 2023
Last chance to get a moon phase calendar! Only a few left.
The invention of different galaxies
The well-known astronomer Edwin P. Hubble first labeled galaxies based mostly on their visible look within the late Nineteen Twenties and 30s. Actually, Hubble’s Classification of Galaxies continues to be extensively used right now. Though, since Hubble’s time, like every efficient classification system, it’s advanced in mild of ongoing observations. Hubble used a number of fundamental kinds of galaxies, every containing sub-types.
Spiral galaxies are extra mysterious than we thought! @KarenLMasters, @vrooje and a whole bunch of 1000’s of volunteers @GalaxyZoo have proven that the ‘Hubble Tuning Fork’ methodology of categorisation is fallacious ??https://t.co/EUu9BhBUef pic.twitter.com/QFZgrXHjtU
— Royal Astronomical Society (@RoyalAstroSoc) June 11, 2019
Earlier than Hubble’s examine of galaxies, we believed that our galaxy was the one one within the universe. Astronomers thought that the smudges of sunshine they noticed by their telescopes have been actually nebulae inside our personal galaxy. Nevertheless, Hubble found that these nebulae have been galaxies. Moreover, it was Hubble who demonstrated, by measuring their velocities, that they lie at huge distances from us.
These galaxies lie thousands and thousands of light-years past the Milky Way, at distances so big they seem tiny in all however the largest telescopes. Furthermore, he demonstrated that, wherever he appeared, galaxies have been receding from us in all instructions, and the additional away they’re, the sooner they’re receding. Thus, Hubble had found that the universe is expanding.
Spiral galaxies
The commonest kind of galaxy is a spiral galaxy. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. Spiral galaxies have majestic, sweeping arms, 1000’s of sunshine years lengthy, made up of thousands and thousands upon thousands and thousands of stars. Their spiral arms stand out due to shiny stars, glowing fuel and dust. Spiral galaxies are energetic with star formation.
Additionally, spiral galaxies have a shiny heart, made up of a dense focus of stars, so tightly packed that from a distance the galaxy’s heart seems like a stable ball. This ball of stars is named the galactic bulge.
Additionally, there are two kinds of spiral galaxies. There are common spirals and barred spirals. If the spiral has bars, they prolong off the central bulge. Then, the spiral arms begin on the finish of the bar.
Elliptical and irregular galaxies
Elliptical galaxies are the universe’s largest galaxies. Actually, large elliptical galaxies will be about 300,000 light-years throughout. Whereas, the dwarf elliptical galaxies – the most typical elliptical – are only some thousand light-years throughout. There are a number of shapes of elliptical galaxies, starting from round to football-shaped.
General, 1/3 of all galaxies are elliptical galaxies. Elliptical galaxies comprise little or no fuel and dust – in comparison with a spiral or irregular galaxy – and they’re not actively forming stars. The celebs in elliptical galaxies are older stars and comprise only a few heavier parts.
Irregular shaped galaxies have all kinds of various shapes however they don’t appear like a spiral or elliptical galaxy.
Irregular galaxies can have little or no dust or rather a lot. Plus, they will present energetic star-forming areas or have little-to-no star formation occurring. They appeared plentiful within the early universe.
Our Milky Way Galaxy
The Milky Way, actually, falls into considered one of Hubble’s spiral galaxy sub-types: it’s a barred spiral, which suggests it has a bar of stars protruding out from all sides of its heart. Because the spiral arms sweep out of their swish and large arcs, the ends of the bars are the anchors. This can be a current discovery and it’s unknown how bars type in a galaxy. Our solar system is located about 2/3 of the way in which out from the galactic heart in direction of the periphery of the galaxy, embedded in considered one of these spiral arms.
One other current discovery is that the disk of the Milky Way is warped, like a long-playing vinyl file left too lengthy within the sun. Precisely why is unknown, however it could be the results of a gravitational encounter with one other galaxy early within the Milky Way’s historical past.
It additionally seems that each one galaxies rotate. For instance, the Milky Way takes 226 million years to spin round as soon as. Since its creation, the Earth has traveled 20 occasions across the galaxy.
Galaxies are available in clusters
Galaxies group collectively in clusters. Our personal galaxy is a component of what’s referred to as the Local Group, and it accommodates roughly 55 galaxies.
In the end, galaxy clusters themselves group into superclusters. Our Native Group is a part of the Virgo Supercluster.
The “glue” that binds stars into galaxies, galaxies into clusters, clusters into superclusters and superclusters into filaments is – after all – gravity. Actually, gravity is the universe’s development employee, which sculpts all of the buildings we see within the cosmos.
The Universe is Infinite. Nevertheless our existence in our present Galaxy Cluster is Finite. Time can be an element… Our Galaxy Clusters truly increase into the void of space over time. pic.twitter.com/EAOcisPdZn
— Gustavo Suárez (@gsuarez333) February 26, 2023
Galaxies are flying aside
Though most galaxies are flying aside from one another, these astronomically shut to one another will probably be gravitationally sure to one another. Caught in an inexorable gravitational dance, finally they merge, passing by one another over thousands and thousands of years, finally forming a single, amorphous elliptical galaxy. Gravity shockwaves compress big clouds of interstellar fuel and dust throughout such mergers, giving rise to new generations of stars.
The Milky Way is caught in such a gravitational embrace with M31, aka the Andromeda galaxy, which is 2 1/2 million light-years distant. Each galaxies are shifting towards one another due to gravitational attraction: they’ll merge in about 6 billion years. Nevertheless, each galaxies are surrounded by big halos of fuel which can prolong for thousands and thousands of light-years, and it was discovered that the halos of the Milky Way and M31 have already began to the touch.
Galaxy mergers and companion galaxies
Galaxy mergers are widespread. The universe is stuffed with examples of galaxies in varied levels of merging collectively, their buildings disrupted and distorted by gravity, forming weird and exquisite shapes.

Then, on the decrease finish of the galactic dimension scale, there are so-called dwarf galaxies, consisting of some hundred to as much as a number of billion stars. Their origin isn’t clear. Usually, they haven’t any clearly outlined construction. Astronomers imagine they have been born in the identical manner as bigger galaxies just like the Milky Way, however for no matter motive they stopped rising. Ensnared by the gravity of a bigger galaxy, they orbit its periphery. The Milky Way has round 20 dwarf galaxies orbiting it that we all know of, though some fashions predict there needs to be many extra.
Our closest neighbors: The Magellanic Clouds
The 2 most well-known dwarf galaxies for us earthlings are, after all, the Small and Large Magellanic Clouds, seen to the unaided eye in Earth’s Southern Hemisphere sky.
Finally, these and different dwarf galaxies will rip aside beneath the titanic pull of the Milky Way’s gravity. This may go away behind a barely noticeable stream of stars throughout the sky, slowly dissipating over eons.

Supermassive black holes lurk in galactic facilities
On the heart of most galaxies lurks a supermassive black hole, of thousands and thousands and even billions of solar plenty. For instance, TON 618, has a mass 66 billion occasions that of our sun.
The origin and evolution of supermassive black holes stays a thriller. Just a few years in the past, astronomers uncovered a shocking truth: in spiral galaxies, the mass of the supermassive black hole has a direct linear relationship with the mass of the galactic bulge. The extra mass the black hole has, the extra stars there are within the bulge. Nobody is aware of precisely what the importance of this relationship could also be. Nevertheless, its existence appears to point that the expansion of a galaxy’s stellar inhabitants and that of its supermassive black hole are inextricably linked.
This discovery comes at a time when astronomers are starting to appreciate {that a} supermassive black hole could management the destiny of its host galaxy: the copious quantities of electromagnetic radiation emitted from the maelstrom of fabric orbiting the central black hole, referred to as the accretion disk, could push away and dissipate the clouds of interstellar hydrogen from which new stars type. This acts as an inhibitor on the galaxy’s potential to present delivery to new stars. In the end, the emergence of life itself could also be tied to the exercise of supermassive black holes. That is an space that’s present process intensive analysis.
Whereas astronomers nonetheless know little or no about precisely how galaxies formed within the first place – we see them of their nascent state only some hundred million years after the Large Bang – the examine of galaxies is an countless voyage of discovery.
We found different galaxies exist lower than a century in the past
Lower than 100 years after we realized that different galaxies exist apart from our personal, we’ve discovered a lot about these grand, majestic star cities. And there may be nonetheless a lot to be taught.
Backside line: A galaxy is an unlimited island of fuel, dust and stars in an ocean of space. There are three kinds of galaxies. Study these starry islands in space.
Read more: Milky Way’s farthest stars reach halfway to Andromeda



